Quality
Top quality is a daily mission
Remo aims for the continuous improvement of products and services every day. The quality must constantly be of the highest level. Absolute food safety must be guaranteed. Customers may not find any variations. Training, a specific centralised quality system and specifically developed ICT applications guarantee quality monitoring and support the quality department and the management.
Audits from field to door
This vision was also laid down in the company's quality statement. In addition, Remo expressly sought to obtain the strict BRC certificate based on the HACCP-principles.
Remo regularly invites auditors from independent auditing organisations to inspect the processes. Because quality starts with the ingredients, Remo works exclusively with GlobalGap and/or Vegaplan certified growers. Remo's own potato field obviously also has the required certificates.
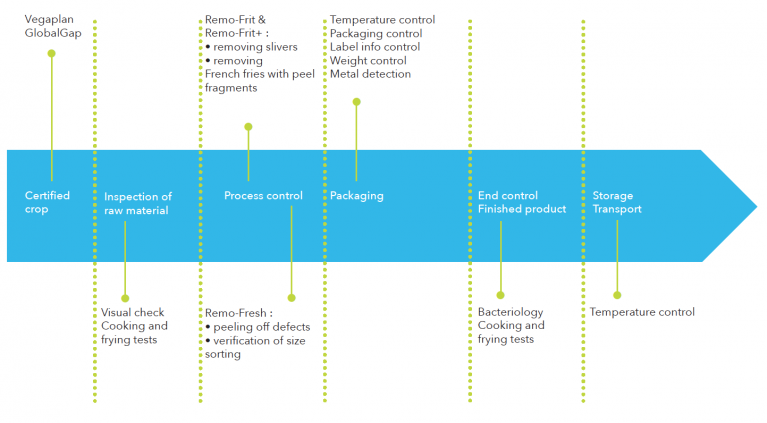
During the process from rough to finished product a large amount of inspections are provided. It starts when the purchased potatoes are inspected by the growers and ends with the delivery of cooled truck loads at your gate.
Ultramodern machinery
A top product requires the best raw material and the most modern machinery and techniques. Remo has ultramodern and efficient machinery at all sites. This allows us to go for the top quality you are counting on every day. Even in difficult circumstances (seasonal variations) and while maintaining the familiar flexibility. An innovative, sustainable vision is crucial in this aim. Therefore, Remo is constantly working on new techniques and is partner in a number of university research projects.
Certification
BRC

In 1998 the British Retail Consortium (BRC) developed a food safety standard, the BRC standard. The BRC standard is based on the HACCP principles and imposes a number of additional requirements on several topics, including:
- The involvement of higher management.
- The food safety plan.
- The production facilities.
- Product control.
- Process control.
- Staff.
HACCP
HACCP, the abbreviation for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points, is a risk inventory for food products. Businesses involved in the preparation, processing, treatment, packaging, transport and distribution of food products must therefore identify all aspects of the production process and analyse the hazards. This control process, set up by the European Union, wants to ensure that the production process of all food products involves a minimum of contamination risks. For example, the continuous monitoring and registering of cooling and freezing cells has become mandatory as a result.
The 7 principles of an HACCP system:
- Take stock of all potential hazards.
- Define the critical control points (CCPs), the points in the process where the risk can be avoided or restricted.
- Indicate the critical margins for each CCP.
- Define how the CCPs must be monitored.
- Define corrective actions for each CCP which must restore the safety.
- Apply verification, a regular check to verify whether the HACCP approach is working adequately.
- Keep all documentation and registrations. Record the adjustment you made and how you made them.
By means of the contact form you can get access to the different certifications.

